Applications of Optical Switch Technology
https://www.feiyi-oeo.com/product-category/polarization-maintaining/pm-photoswitch
With the development of fiber optic communication technology and the application of Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) systems, optical networking has become a trend in network development. The realization of optical networking technology primarily relies on the advancement of devices and technologies such as optical switches.
Key Application Areas of Optical Switches
The application of optical switches permeates the entire optical communication system, from long-haul backbone networks to data centers.Optical Network Protection and Restoration
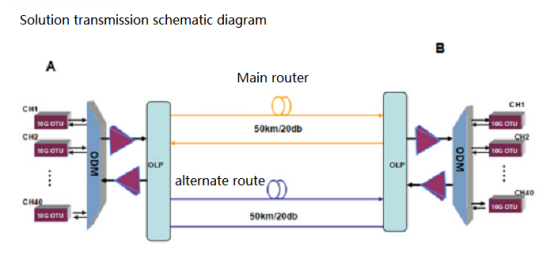
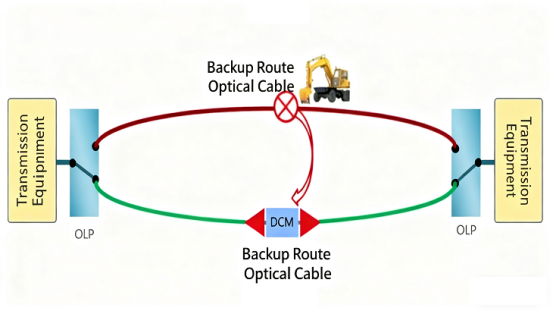
Scenario: When a fiber network breaks due to construction, natural disasters, etc., services need to be rapidly switched to backup fibers.
Application: Deploy optical switches (typically mechanical or MEMS) at key network nodes. Once a primary fiber failure is detected, the control system triggers the optical switch within tens of milliseconds to route the optical signal to a backup path, ensuring uninterrupted communication.
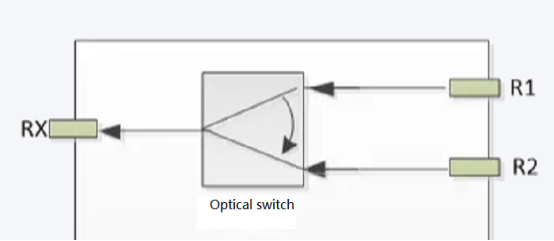
Optical Cross-Connect (OXC)
Scenario: At core network nodes (e.g., OXC equipment), dynamic and flexible configuration of connection relationships between numerous fibers is required.
Application: Using large-scale optical switch arrays (e.g., MEMS optical switches) enables connections from any input port to any output port, greatly enhancing network flexibility and resource utilization. This is fundamental for building intelligent, reconfigurable optical networks.
Network Monitoring and Testing
Scenario: Operators need to monitor network performance and diagnose faults without interrupting normal services.
Application: Use optical switches to build an automated testing platform. By programmatically controlling optical switches, different fibers in the network can be sequentially connected to a shared test device (e.g., Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer or Optical Spectrum Analyzer), achieving “one-to-many” centralized monitoring and saving significant equipment and labor costs.
Data Center Optical Switching
Scenario: Modern data centers contain a vast number of servers with massive east-west traffic (between servers), demanding extremely high bandwidth and low latency.
Application: Traditional electrical switching faces bottlenecks in power consumption and bandwidth. Optical Circuit Switching uses large-scale, low-loss optical switches (e.g., MEMS) to dynamically establish direct optical connections between server clusters within the top-level network architecture, providing high-bandwidth, low-latency channels, particularly suitable for scenarios like AI computing and big data transmission.

Sensing Systems
Scenario: In fiber optic sensing networks (e.g., perimeter security, pipeline monitoring), there is a need to monitor multiple points using a single fiber.
Application: Optical switches are used to switch between different sensing
