Basic Principles of WDM Technology
https://www.feiyi-oeo.com/product-category/passive-device/wdm
WDM, or Wavelength Division Multiplexing, is a cutting-edge and mature optical fiber communication technology widely used in commercial applications today. This article aims to dissect the principles of WDM for you, guiding you into the core technology of the optical communication field.
The principle of WDM technology can be understood through the following steps:
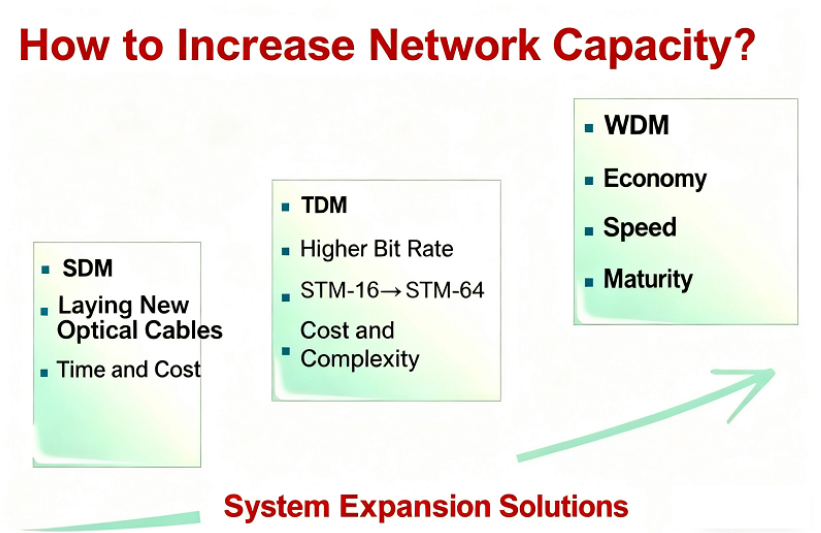
SDM (Space Division Multiplexing) increases transmission capacity linearly by adding more fibers, but this also means transmission equipment must increase correspondingly and linearly.
TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) has evolved from the primary to quaternary multiplexing groups of traditional PDH to the STM-1, STM-4, STM-16, and even STM-64 multiplexing of SDH. However, this technology also has some shortcomings, including potential service disruption, inflexibility in rate upgrades, and the high cost of high-rate TDM equipment, especially as 40Gbit/s TDM equipment approaches the speed limit of electronic devices.
WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing), on the other hand, allows optical signals of different rates (wavelengths) to be mixed together for transmission. By introducing new wavelength characteristics, WDM can flexibly determine network capacity according to user needs.

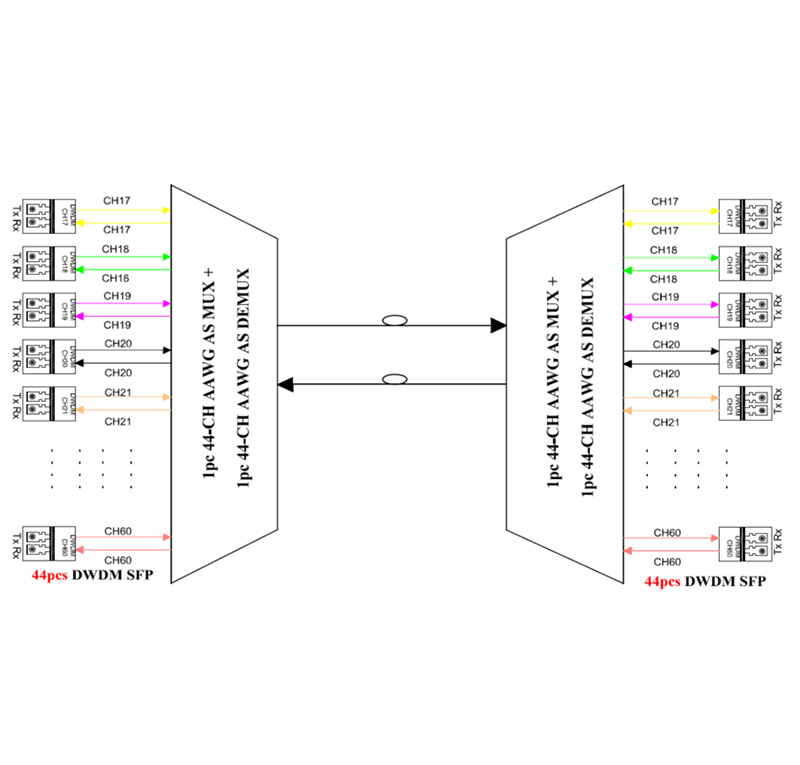
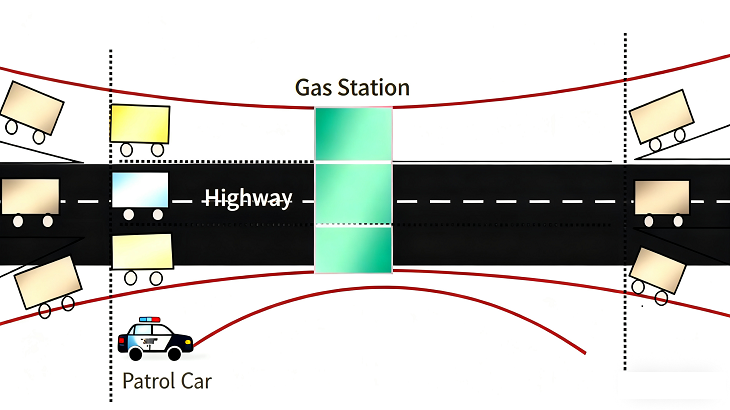
To better understand the specific meaning of Wavelength Division Multiplexing technology, we can use an analogy with a highway: a single optical fiber is seen as a “multi-lane” public road, where light signals of different wavelengths are like vehicles in different lanes, which can travel simultaneously in the same fiber without interfering with each other.
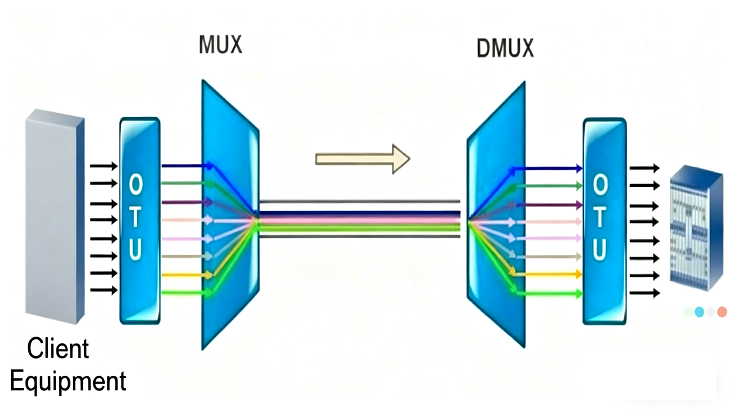
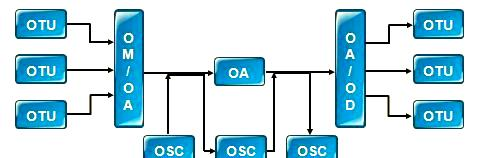
◇ WDM System Structure and Configuration
A WDM system includes components such as optical wavelength conversion units, optical multiplexers/demultiplexers, optical amplifiers, and
optical/electrical supervisory channels, which enable signal multiplexing and transmission.
The structure of a WDM system is outlined as follows:
Optical Wavelength Conversion Unit (OTU): Responsible for signal conversion and processing.
Optical Multiplexer/Demultiplexer (ODU/OMU): Used for combining or separating optical signals.
Optical Amplifier: Provides gain for amplifying optical signals.
Optical/Electrical Supervisory Channel (OSC/ESC): Used to monitor the system’s operational status and performance.
To make the OTU output comply with ITU-T standards, the optical wavelength conversion unit often needs customization to meet customer requirements. The optical multiplexer (optical combiner) and optical demultiplexer are different devices: the former is used for combining waves at the transmitting end, and the latter for separating waves at the receiving end. Optical amplifiers, especially Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs), play a crucial role in optical fiber communication.
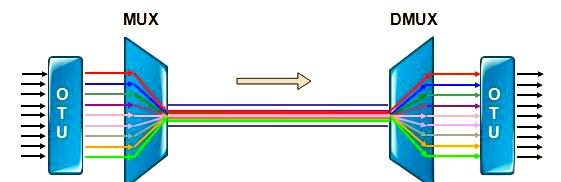
◇ Light Sources and Modulation Methods for WDM Technology
The characteristics of light sources and modulation methods significantly impact WDM system performance. Selecting appropriate light sources and modulation methods ensures the performance and stability of the WDM system.
Electro-Absorption Modulation does not directly modulate the light source but introduces a modulator in the light source’s output path, thereby achieving signal modulation without altering the spectral characteristics of the light wave.
Mach-Zehnder (M-Z) Modulation, on the other hand, utilizes the principle of interference for modulation, offering high speed and high resolution.
It is important to emphasize that different modulation technologies have their own advantages and challenges. In practical applications, choices are usually made based on transmission requirements and system budget.